Does Gum Disease Smell?
If you've ever wondered whether gum disease has a smell, the short answer is: yes, it often does. In fact, persistent bad breath—also known as halitosis—is one of the most common and noticeable symptoms of gum disease. But what exactly causes this odor, and what can you do about it?
The Science Behind the Smell
Gingivitis is inflammation of the gums. Inflamed gums (gingivitis) are often red, swollen, bleed, and are tender. If left untreated, gingivitis may progress in periodontitis. Periodontitis occurs when there is loss of bone that supports the teeth. This will put you at a greater risk for tooth loss.

Gum disease typically starts with plaque buildup, which harbors bacteria. As the disease progresses, these bacteria accumulate in the pockets between your teeth and gums, where they thrive in low-oxygen environments. The bacteria break down the layers of the plaque that contain food remnants, dead cells, mucus, and other bacteria. This process can this release volatile sulfur compounds (VSCs).
Examples of VSCs are hydrogen sulfide and methyl mercaptan—that smell distinctly foul, often compared to rotten eggs, garlic, or decay. Tissue death also adds to the smell when there is a breakdown of the gum tissue, ligaments, and even bone. This is why people with gum disease may notice a persistent, unpleasant odor coming from their mouths, even after brushing or using mouthwash. Sometimes this is referred to as Perio Breath.
Bad breath is not always caused by gum disease.
Other causes include
- Tooth decay
- Bacteria on the tongue
- Infections in the mouth
- Medications that cause dry mouth
- Disorders that cause dry mouth related to reduced saliva production like diabetes or Sjogren’s syndrome.
- Non-oral causes of bad breath are linked to many different body systems (i.e. diabetes, liver disease, acid reflux, etc.). It could also be related to infections in the ear, nose, or throat.
- Poor oral hygiene
- Other causes of bad breath are often temporary. These may include strong flavored food, drinks such as coffee or alcohol, or tobacco products.
Signs that your bad breath might be gum disease.
While bad breath can have many causes, here are some signs that it might be linked to gum disease:
- Red, swollen, or bleeding gums
- Receding gum lines
- Loose or shifting teeth
- A persistent sour or metallic taste
- Visible plaque or tartar buildup
Treatment of bad breath.
If you’ve noticed persistent bad breath or other signs of gum disease, don’t ignore them. Visit your dental professional to receive a proper diagnosis. Your mouth—and your overall health—will thank you. Improving your oral hygiene by brushing, cleaning between the teeth, cleaning your tongue, and using mouth wash can decrease your risk of having bad breath when it is related to an oral cause.
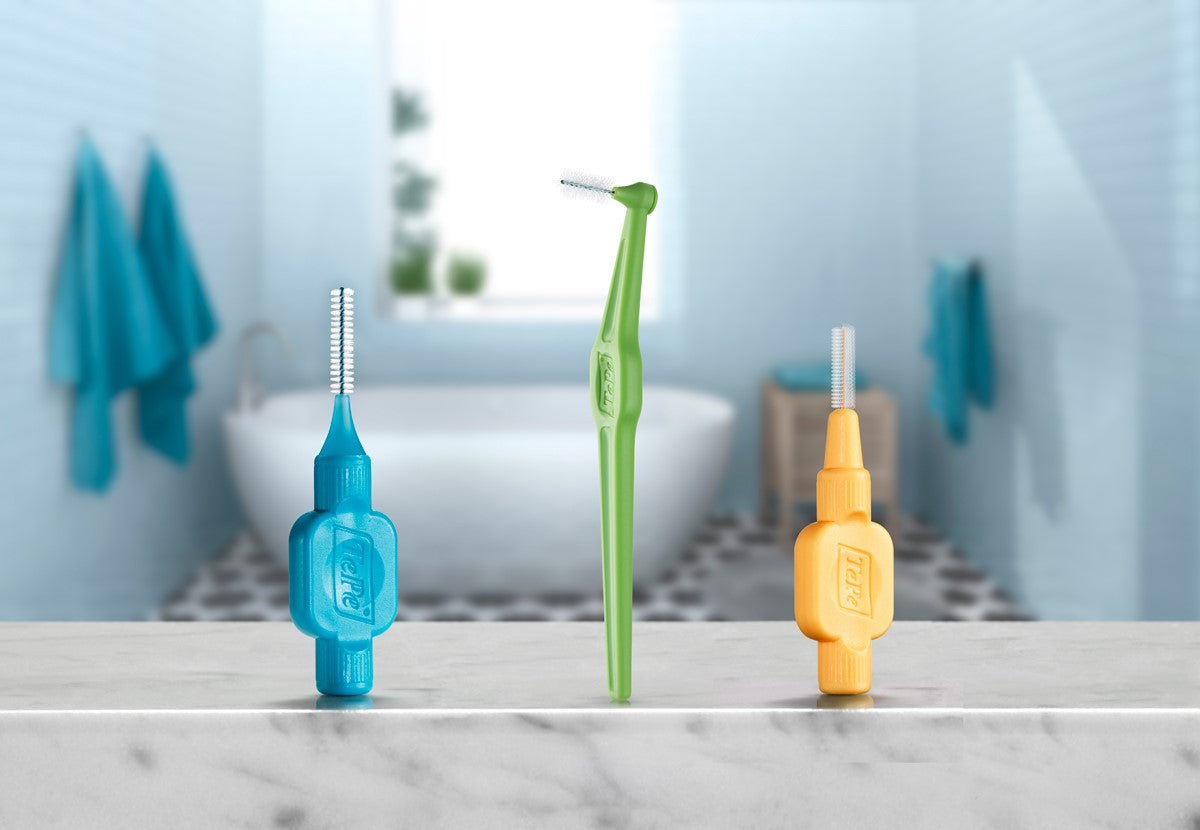
Bacteria that thrive on the top surface of the tongue can be removed by using the TePe® Tongue Cleaner. The design corresponds to the natural shape of the tongue and the 3 blades give it a triple effect with one stroke.

Bacteria and plaque between the teeth can be removed using TePe Interdental Brushes. These small brushes clean where a regular toothbrush does not reach. TePe has nine different size brushes to fit all varieties of spaces between teeth.

Read More:
Determining the association between oral malodor and periodontal disease: A case control study - PMC
Halitosis: From diagnosis to management - PMC










Leave a comment