How Does a Periodontist Treat Gum Disease?
Gum disease, also known as periodontal disease, is a prevalent condition affecting millions worldwide. Thankfully, with the expertise of a skilled periodontist and proper oral hygiene, gum disease can be effectively treated and managed.
Understanding Gum Disease
Gum disease is a progressive condition that affects the gums and the supporting structures of the teeth. It starts with plaque buildup on the teeth, which, if not removed promptly through regular brushing and cleaning between the teeth, can lead to the formation of tartar (hardened plaque). The bacteria in plaque and tartar cause inflammation of the gums, leading to the early stage of gum disease known as gingivitis. If left untreated, gingivitis can progress into periodontitis, a more severe form of gum disease that results in bone loss. This can lead to tooth loss and other serious oral health issues.
The Role of a Periodontist
A periodontist is a dental specialist who focuses on the prevention, diagnosis, and treatment of gum diseases and the placement of dental implants. After completing dental school, periodontists undergo several years of additional training in periodontal procedures and surgical techniques. This specialized knowledge and experience make them experts in handling various gum-related issues effectively.
Diagnosing Gum Disease
When you visit a periodontist, they will start by conducting a thorough examination of your gums and teeth. They will check for signs of inflammation, recession, pocket formation (spaces between the gums and teeth),and assess the level of tartar buildup. X-rays will also be taken to evaluate the bone supporting the teeth and to detect any hidden issues. Your dental professional will review your medical history and any other possible contributing risk factors.
Treatment Options
The treatment approach recommended by the periodontist will depend on the severity of the gum disease and the patient's individual needs. Here are some common treatment options:
1. Scaling and Root Planing (Deep Cleaning)
In the early stages of gum disease, a thorough professional cleaning called scaling and root planing may be sufficient. This process involves removing plaque and tartar from above and below the gumline and smoothing the root surfaces to prevent bacterial buildup.
2. Periodontal Surgery
In advanced cases, where gum disease has caused significant damage, periodontal surgery may be required. Some common surgical procedures include flap surgery (lifting the gums to clean the roots and repositioning them) and bone grafts (to regenerate lost bone structure).
3. Dental Implants
For patients who have experienced tooth loss due to gum disease, a periodontist can place dental implants to replace the missing teeth effectively.
4. Ongoing Maintenance
After treatment, the periodontist will work closely with the patient to develop a personalized maintenance plan. Regular check-ups and cleanings are essential to monitor progress and ensure the disease does not return.
The Importance of Prevention
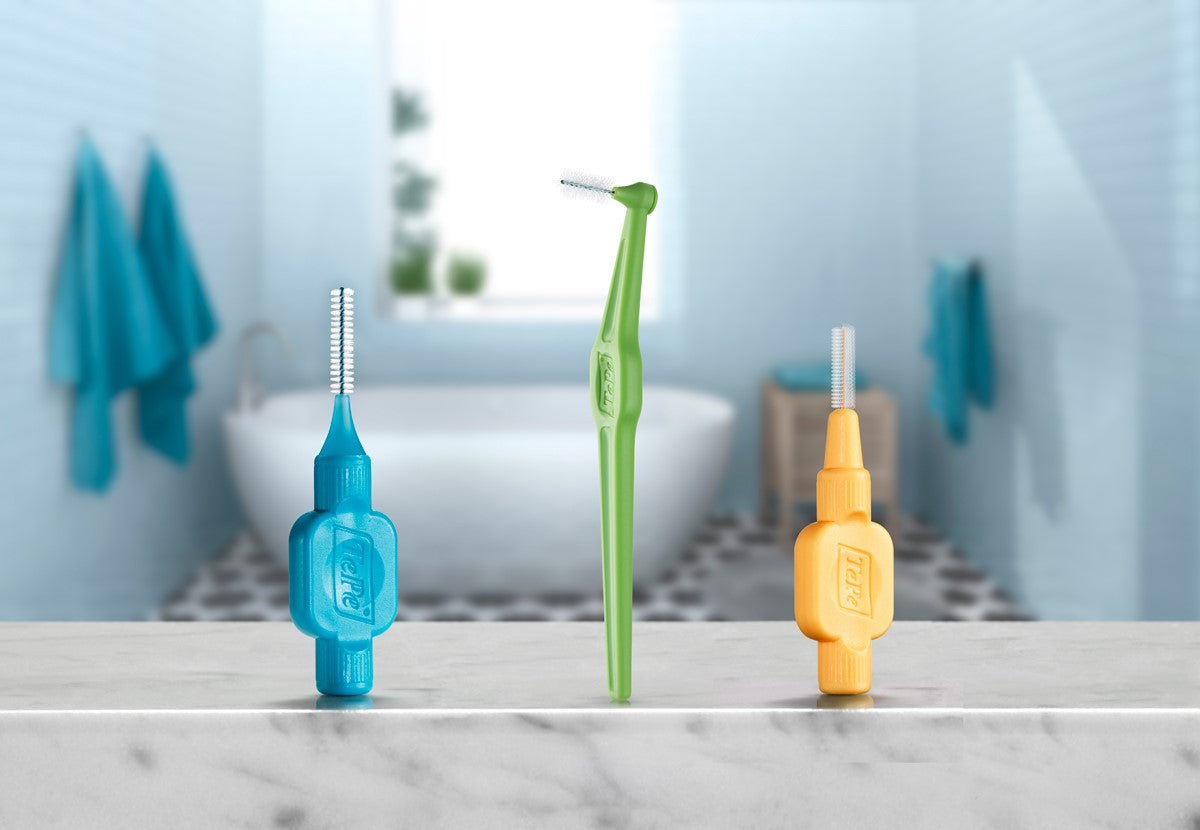
Prevention is always better than treatment when it comes to gum disease. Regular dental check-ups, proper oral hygiene practices, and a balanced diet can significantly reduce the risk of gum disease and other oral health issues. Brushing twice a day and cleaning between the teeth and implants, for example using TePe interdental brushes, are crucial components of a comprehensive oral care routine.
Periodontists play a pivotal role in treating gum disease, ensuring patients receive the specialized care they need to combat this prevalent condition. If you suspect gum disease or have any concerns about your oral health, don't hesitate to consult with an experienced periodontist.










Leave a comment